Incoterms®
Incoterms® are a series of regulations published by the International Chamber of Commerce ( ICC ) which define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international commercial transactions.
General Information
Incoterms® are a series of regulations published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) for use in international commercial transactions. The first edition was published in 1936. These regulations are reviewed approximately every ten years to ensure they reflect current world trade practices whilst also making them more accessible and easier to use.
Goods move across international borders as a result of a sale involving a buyer and a seller. The contract of sale should define the responsibilities of both parties in respect of both the physical nature of the goods and the movement of the consignment. The buyers and sellers have various options open to them as defined by Incoterms®.
Incoterms® clarify the tasks, costs and risks to be borne by the buyer and seller and identify at which point these risks transfer to another party.
A new edition, Incoterms® 2020, became effective as of the 1st January 2020. As of this date all sales contracts should make reference to Incoterms® 2020 sales terms.
There are two categories from which Incoterms® users identify the correct terms for their particular requirements.
The two categories cover:
Terms for any Mode or Modes of Transport
Terms for Sea and Inland Waterway Transport
Incoterms® are a series of regulations published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) for use in international commercial transactions. The first edition was published in 1936. These regulations are reviewed approximately every ten years to ensure they reflect current world trade practices whilst also making them more accessible and easier to use.
Goods move across international borders as a result of a sale involving a buyer and a seller. The contract of sale should define the responsibilities of both parties in respect of both the physical nature of the goods and the movement of the consignment. The buyers and sellers have various options open to them as defined by Incoterms®.
Incoterms® clarify the tasks, costs and risks to be borne by the buyer and seller and identify at which point these risks transfer to another party.
A new edition, Incoterms® 2020, became effective as of the 1st January 2020. As of this date all sales contracts should make reference to Incoterms® 2020 sales terms.
There are two categories from which Incoterms® users identify the correct terms for their particular requirements.
The two categories cover:
Terms for any Mode or Modes of Transport
Terms for Sea and Inland Waterway Transport
Incoterms® 2020
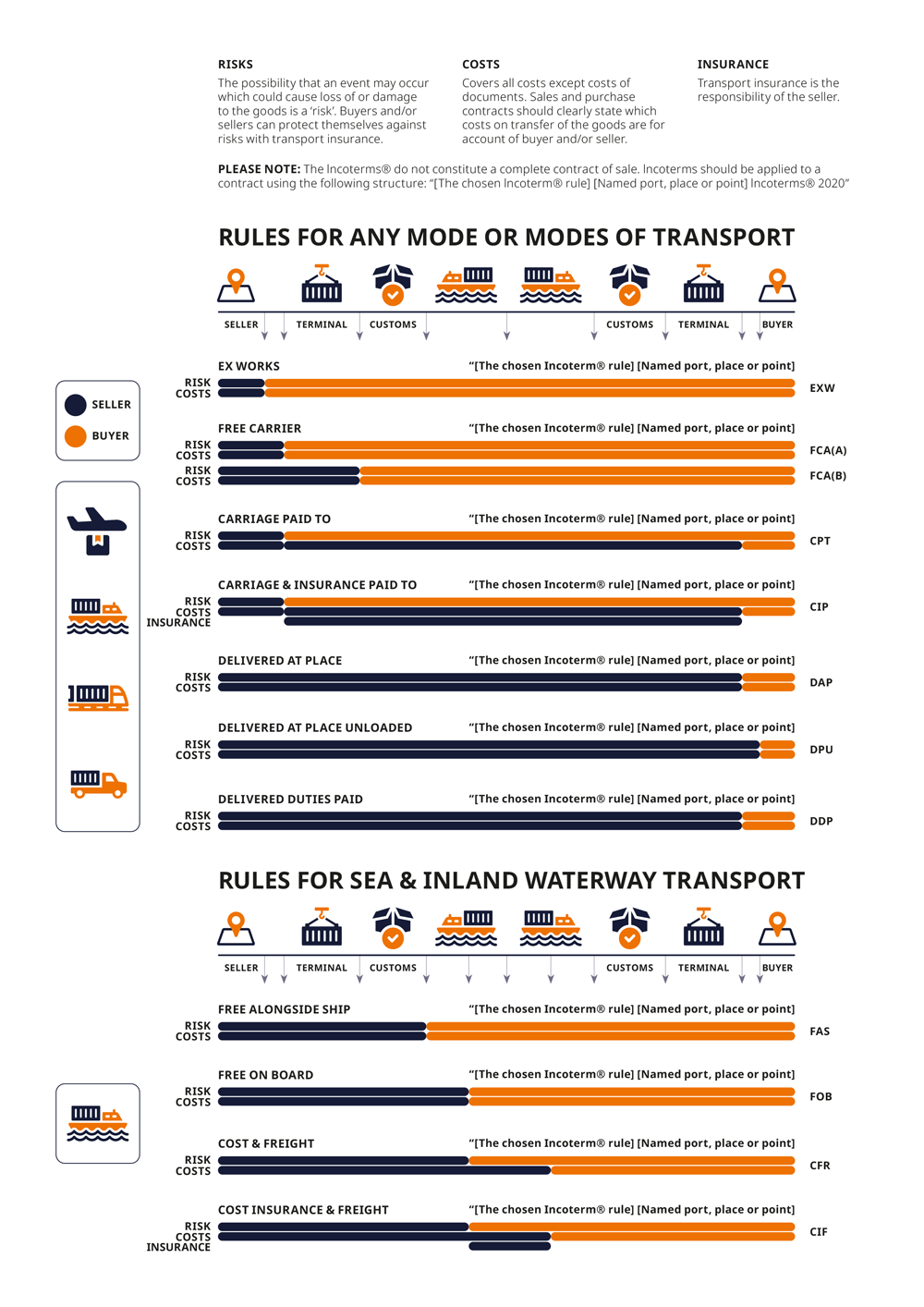
There are 11 Incoterms®, as with Incoterms® 2010. Please refer to the below terms.
Terms for any Mode or Mode of Transport
Ex Works (EXW)
This rule places minimum responsibility on the seller, who merely has to make the goods available, suitably packaged, at the specified place.
The buyer is responsible for loading the goods onto a vehicle, for all export procedures, onward transport and all costs arising after collection of the goods.
Free Carrier (FCA)
A very flexible rule that is suitable for all situations where the buyer arranges the main carriage to a named place.
In all cases, the seller is responsible for export clearance, the buyer assumes all risks and costs after the goods have been delivered to the named place.
Carriage Paid To (CPT)
The seller is responsible for arranging carriage to the named place, but not for insuring the goods to the named place. Risk transfers from seller to buyer, at the point where the goods are taken in charge by a carrier.
Carriage and Insurance Paid To (CIP)
The seller is responsible for arranging carriage to the named place, and also for insuring the goods.
Risk transfers from seller to buyer, at the point where the goods are taken in charge by a carrier.
Delivered at Place (DAP)
The seller is responsible for arranging carriage and for delivering the goods, ready for unloading from the arriving means of transport, at the named place.
Risk transfers from seller to buyer when the goods are available for unloading; so unloading is at the buyer’s risk.
The buyer is responsible for import clearance and any applicable local taxes or import duties.
Delivered at Place Unloaded DPU
The seller is responsible for arranging carriage and for delivering the goods, unloaded from the arriving means of transport, at the named place.
There are no restrictions on the named place – for example it can be a transport hub, a warehouse or the buyer’s depot.
Risk transfers from seller to buyer when the goods have been unloaded. This is the only rule that requires the seller to unload the goods in order to complete delivery.
The buyer is responsible for import clearance and any applicable local taxes or import duties.
Delivered Duty Paid (DDP)
The seller is responsible for arranging carriage and delivering the goods at the named place, cleared for import and all applicable taxes and duties paid (e.g. VAT, GST)
Risk transfers from seller to buyer when the goods are made available to the buyer, ready for unloading from the arriving means of transport.
This rule places the maximum obligation on the seller, and is the only rule that requires the seller to take responsibility for import clearance and payment of taxes and/or import duty.
Free Alongside Ship (FAS)
Seller delivers goods, cleared for export, alongside the vessel at a named port, at which point risk transfers to the buyer.
The buyer is responsible for loading the goods and all costs thereafter.
Free On Board (FOB)
Seller delivers goods, cleared for export, loaded on board the vessel at the named port.
Once the goods have been loaded on board, risk transfers to the buyer, who bears all costs thereafter.
Cost and Freight (CFR)
Seller arranges and pays for transport to named port. Seller delivers goods, cleared for export, loaded on board the vessel.
Risk transfers from seller to buyer once the goods have been loaded on board, before the main carriage takes place.
Cost Insurance and Freight (CIF)
Seller arranges and pays for transport to named port. Seller delivers goods, cleared for export, loaded on board the vessel.
Risk transfers from seller to buyer once the goods have been loaded on board, before the main carriage takes place.
Seller also arranges and pays for insurance for the goods for carriage to the named port.
These terms all need to specify the place of delivery or destination.
Number of Incoterms®
Incoterms® 2020
There are 11 Incoterms®, as with Incoterms® 2010. Please refer to the below terms.
Terms for any Mode or Mode of Transport
Ex Works (EXW)
This rule places minimum responsibility on the seller, who merely has to make the goods available, suitably packaged, at the specified place.
The buyer is responsible for loading the goods onto a vehicle, for all export procedures, onward transport and all costs arising after collection of the goods.
Free Carrier (FCA)
A very flexible rule that is suitable for all situations where the buyer arranges the main carriage to a named place.
In all cases, the seller is responsible for export clearance, the buyer assumes all risks and costs after the goods have been delivered to the named place.
Carriage Paid To (CPT)
The seller is responsible for arranging carriage to the named place, but not for insuring the goods to the named place. Risk transfers from seller to buyer, at the point where the goods are taken in charge by a carrier.
Carriage and Insurance Paid To (CIP)
The seller is responsible for arranging carriage to the named place, and also for insuring the goods.
Risk transfers from seller to buyer, at the point where the goods are taken in charge by a carrier.
Delivered at Place (DAP)
The seller is responsible for arranging carriage and for delivering the goods, ready for unloading from the arriving means of transport, at the named place.
Risk transfers from seller to buyer when the goods are available for unloading; so unloading is at the buyer’s risk.
The buyer is responsible for import clearance and any applicable local taxes or import duties.
Delivered at Place Unloaded DPU
The seller is responsible for arranging carriage and for delivering the goods, unloaded from the arriving means of transport, at the named place.
There are no restrictions on the named place – for example it can be a transport hub, a warehouse or the buyer’s depot.
Risk transfers from seller to buyer when the goods have been unloaded. This is the only rule that requires the seller to unload the goods in order to complete delivery.
The buyer is responsible for import clearance and any applicable local taxes or import duties.
Delivered Duty Paid (DDP)
The seller is responsible for arranging carriage and delivering the goods at the named place, cleared for import and all applicable taxes and duties paid (e.g. VAT, GST)
Risk transfers from seller to buyer when the goods are made available to the buyer, ready for unloading from the arriving means of transport.
This rule places the maximum obligation on the seller, and is the only rule that requires the seller to take responsibility for import clearance and payment of taxes and/or import duty.
Free Alongside Ship (FAS)
Seller delivers goods, cleared for export, alongside the vessel at a named port, at which point risk transfers to the buyer.
The buyer is responsible for loading the goods and all costs thereafter.
Free On Board (FOB)
Seller delivers goods, cleared for export, loaded on board the vessel at the named port.
Once the goods have been loaded on board, risk transfers to the buyer, who bears all costs thereafter.
Cost and Freight (CFR)
Seller arranges and pays for transport to named port. Seller delivers goods, cleared for export, loaded on board the vessel.
Risk transfers from seller to buyer once the goods have been loaded on board, before the main carriage takes place.
Cost Insurance and Freight (CIF)
Seller arranges and pays for transport to named port. Seller delivers goods, cleared for export, loaded on board the vessel.
Risk transfers from seller to buyer once the goods have been loaded on board, before the main carriage takes place.
Seller also arranges and pays for insurance for the goods for carriage to the named port.
These terms all need to specify the place of delivery or destination.
Click to view
Disclaimer
The information above is based on the information provided on the ICC website; for detailed explanation reference is made to International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) publication INCOTERMS® 2020. This document is provided to our customers for informational purposes only. Please refer to the official text of the ICC for a full and detailed description of all rights and liabilities arising from the use of the aforementioned Incoterms® (https://iccwbo.org).
Find the fastest, most efficient, and cost-effective global shipping solutions with the support of SLA Logistics.
© 2023 SLA Logistics All Rights Reserved
Company Reg No: 07144193 Registered Office: Unit D | Broomshawbury Farms | Hatfield Broad Oak | Essex | CM22 7JY VAT No: GB 985 2867 59